10. Network setup
- VBox:
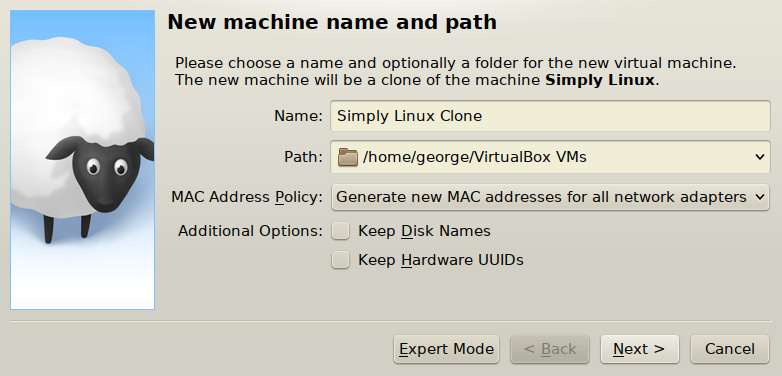
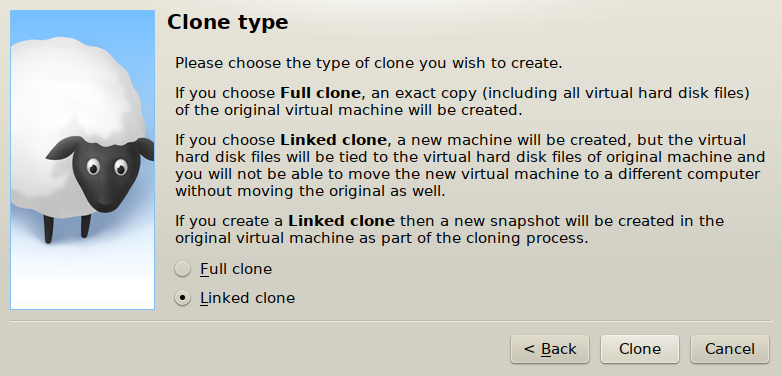
Create a clone of base virtual machine:
- Clone settings
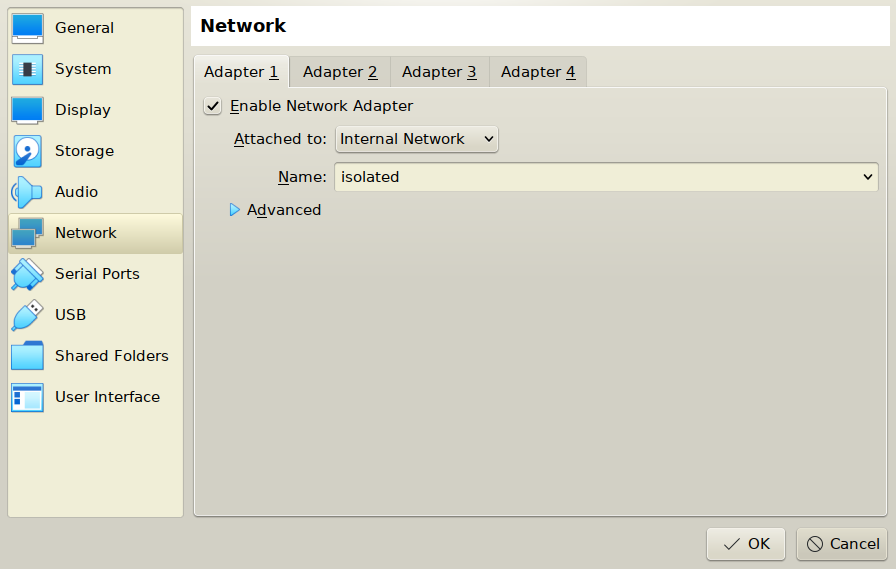
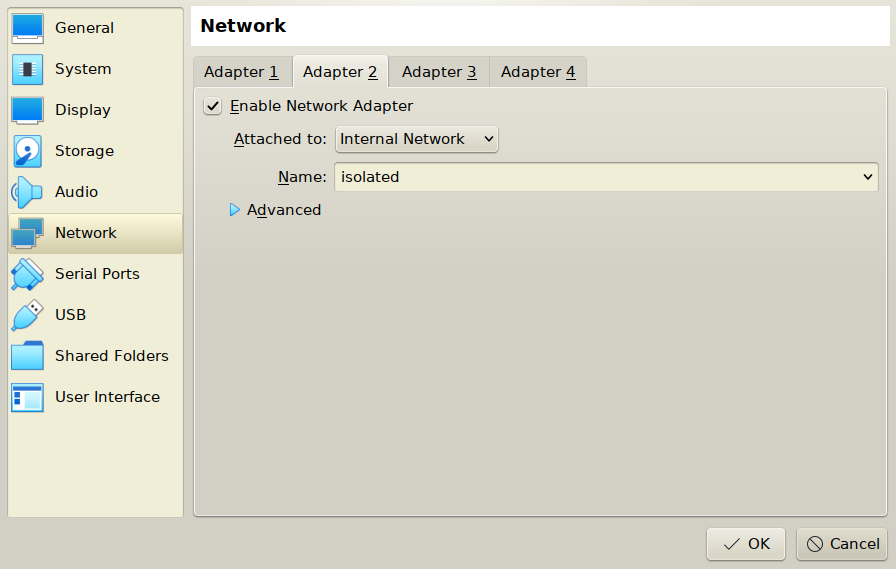
Change network type to Internal
- Clone settings
Add second network interface to base virtual machine
Change it's type to Internal
- Base VM has two network interfaces now:
base, connected both to the Internet and to the isolated network
clone, connected to isolated network only
Boot base
Run ip addr command in terminal to check if:
- There is an IPv4 setup on one of the network interfaces (connected to the internet).
probably eth0 and 10.0.2.15/24; we'll call it ext
- There is no IPv4 setup on the other network interface
probably eth1; we'll call it int
- There is an IPv4 setup on one of the network interfaces (connected to the internet).
Switch to root user
install tcpdump utility with apt-get update; apt-get install tcpdump
 If you cannot, please consult previous labs how to set up a repository
If you cannot, please consult previous labs how to set up a repository
Set up ip address with ip address add devint 192.168.1.2/24
- E. g.:
base ~ # ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:8b:78:f7 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.0.2.15/24 brd 10.0.2.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute eth0 valid_lft 70339sec preferred_lft 70339sec inet6 fe80::5358:7c3d:bdba:9e37/64 scope link noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:f0:55:94 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.1.2/24 scope global eth1 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Boot clone ans switch to root user
Check with ip a if the only network interface has no ip address.
 If it has 10.0.2.something — you probably forgot to change it's type to Internal in the VM setup (see 0.)
If it has 10.0.2.something — you probably forgot to change it's type to Internal in the VM setup (see 0.) It will have name eth0 or eth1 or another, depending on setup, we'll cal it int
Turn off NetworkManager support for this network (right click on nework icon)
This brings int interface down
Bring this interface up by ip link set dev int up
- E. g:
clone ~ # ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state DOWN group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:b9:56:2e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff clone ~ # ip link set dev eth1 up clone ~ # ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:b9:56:2e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:feb9:562e/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
- E. g:
Set up ip address with ip address add dev int 192.168.1.3/24
 Now ping 192.168.1.2 must work from clone to base
Now ping 192.168.1.2 must work from clone to base - E. g.:
clone ~ # ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:b9:56:2e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.1.3/24 scope global eth1 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:feb9:562e/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever clone ~ # ping 192.168.1.2 PING 192.168.1.2 (192.168.1.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.328 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.04 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.941 ms ^C --- 192.168.1.2 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2045ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.328/0.770/1.043/0.315 ms
Routing
No routing (except local) is set up on clone, see ip r
Add default route via base:
clone ~ # ip r 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.3 clone ~ # ping 1.1.1.1 ping: connect: Network is unreachable clone ~ # ip route add default via 192.168.1.2 clone ~ # ip r default via 192.168.1.2 dev eth1 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.3 clone ~ # ping 1.1.1.1 PING 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1) 56(84) bytes of data. --- 1.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 1020ms
 Do not kill ping for not, let it ping!
Do not kill ping for not, let it ping!
VM base is not configured to be router, so:
Use tcpdump -i int to see if pings are accepted by base (they are):
clone ~ # ip route add default via 192.168.1.2 clone ~ # ping 1.1.1.1 PING 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1) 56(84) bytes of data. ^C --- 1.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 2053ms clone ~ # ip r default via 192.168.1.2 dev eth1 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.3 clone ~ # ping 1.1.1.1 PING 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1) 56(84) bytes of data. ^C --- 1.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 1020ms
Use tcpdump -i ext to see if pings are not forwarded by base
Set up base kernel to perform routing with either sysctl ot just echoing 1 into special /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward file
base ~ # cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward 0 base ~ # sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 base ~ # cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward 1
Now tcpdump -i ext will show that pings are forwasrded into outer space with no replies:
base ~ # tcpdump -i eth0 tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 23:27:55.875870 IP 192.168.1.3 > one.one.one.one: ICMP echo request, id 5, seq 605, length 64 23:27:56.900062 IP 192.168.1.3 > one.one.one.one: ICMP echo request, id 5, seq 606, length 64 ^C
 That means routing works, but packets with 192.168.1.3 source address are just dropped (see Private_network)
That means routing works, but packets with 192.168.1.3 source address are just dropped (see Private_network)
- A couple of complexity bits:
First: our 10.0.2.15 address is private too, but internet works! Apparently next router (10.0.2.2):
Has wide area network address (so called white IP)
Performs Network_address_translation over 10.0.2.15 with firewall
Second: this NAT can translate 10.something addresses, but not 192.168.something ones. So we must set up our own firewall NAT!
Call iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o ext -j MASQUERADE:
base ~ # iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE base ~ # iptables-save # Generated by iptables-save v1.8.3 on Wed May 20 23:38:20 2020 *nat :PREROUTING ACCEPT [1:84] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE COMMIT # Completed on Wed May 20 23:38:20 2020
- Now:
 Ping from clone starts working!
Ping from clone starts working! clone ~ # ping 1.1.1.1 PING 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 1.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=7.90 ms 64 bytes from 1.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=61 time=7.78 ms
tcpdump -i ext will show ping traffic as originating from 10.0.2.15:
base ~ # tcpdump -ni eth0 tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 23:42:58.206618 IP 10.0.2.15 > 1.1.1.1: ICMP echo request, id 7, seq 1, length 64 23:42:58.212870 IP 1.1.1.1 > 10.0.2.15: ICMP echo reply, id 7, seq 1, length 64 23:42:59.208748 IP 10.0.2.15 > 1.1.1.1: ICMP echo request, id 7, seq 2, length 64 23:42:59.213064 IP 1.1.1.1 > 10.0.2.15: ICMP echo reply, id 7, seq 2, length 64 23:43:00.210707 IP 10.0.2.15 > 1.1.1.1: ICMP echo request, id 7, seq 3, length 6
Actually, firewall is detecting NAT-ed packages, translate addresses back and then route them to clone, so tcpdump -i int will show it:
base ~ # tcpdump -ni eth1 tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on eth1, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 23:45:35.848024 IP 192.168.1.3 > 1.1.1.1: ICMP echo request, id 8, seq 1, length 64 23:45:35.852829 IP 1.1.1.1 > 192.168.1.3: ICMP echo reply, id 8, seq 1, length 64 23:45:36.848888 IP 192.168.1.3 > 1.1.1.1: ICMP echo request, id 8, seq 2, length 64
DNS
DNS on clone still not working:
clone ~ # ping ya.ru ping: ya.ru: Name or service not known clone ~ # host ya.ru Host ya.ru not found: 5(REFUSED) clone ~ # cat /etc/resolv.conf # Generated by resolvconf # Do not edit manually, use # /etc/net/ifaces/<interface>/resolv.conf instead. nameserver 127.0.0.1
This nameserver 127.0.0.1 means that there is local DNS server on clone (listening on loopback interface), but it is miscionfigured
Ignore it! Just change 127.0.0.1 to 1.1.1.1 (or 8.8.8.8) — popular world-wide DNS servers with your favorite text editor, and then it will work
clone ~ # cat /etc/resolv.conf # Generated by resolvconf # Do not edit manually, use # /etc/net/ifaces/<interface>/resolv.conf instead. nameserver 8.8.8.8 clone ~ # host ya.ru ya.ru has address 87.250.250.242 ya.ru has IPv6 address 2a02:6b8::2:242 ya.ru mail is handled by 10 mx.yandex.ru. clone ~ # ping ya.ru PING ya.ru (87.250.250.242) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from ya.ru (87.250.250.242): icmp_seq=1 ttl=61 time=11.1 ms 64 bytes from ya.ru (87.250.250.242): icmp_seq=2 ttl=61 time=12.5 ms ^C