Homework remaining after classes
Homework tasks should be stored/copied in corresponded directories, named after class topic. All binaries should work on the sugon server.
See >>> link to classes pages.
>>>
- Research
What exit status the command read generates? Try it
Important: Please consult help read (e. g. here) command instead of man read, because read is shell built-in and you got manual page on all shell builtins
- Research
How to suppress «\n» output after echo (see echo)?
- Task
Write a c8 script that asks user for name, and prints a welcome message either if an user has entered a name or not:
Hint: In second example user had not pressed «Enter»
>>>
Create 01_UsingVirtualbox on sugon server
- Run VM
- Open terminal inside vm
Enter command ip link show dev eth0
Create 01_UsingVirtualbox/mac file containing the output of your VM's ip link command
- Copy+paste may work
scp also may work

- Make a vitrualbox snapshot of the installed system
>>>
TODO
>>>
- Complete all tasks
expr again

Write a shell script sumsum.sh that
Has function sum() that
- sums all of it's arguments (any number of arguments are permitted)
- prints this sum if there's no errors
prints 0 if there was error (e. g. try to sum non-numbers)
redirects all error messages to /dev/null
- Reads two lines of numbers
- Prints if their sums was equal or not
>>>
Create 04_VirtualBox2 folder on sugon server. All files should reside there.
Save the contents of the /proc/cmdline file to the cmdline file
Save the output of the systemctl status sshd command to sshd-status file
Copy the /etc/group and /etc/passwd files
To copy files to a folder on a remote server, use the scp command:
$ scp /path/to/local/file username@hostname:/path/to/remote/file $ scp username1@hostname1:/path/to/file username2@hostname2:/path/to/other/file
For example:
$ scp -P 2131 /etc/passwd andrey@sugon:/home/andrey/04_VirtualBox2/
>>>
Complete all tasks. Pay your attention at last tasks (check if the system has virtualbox-addition-guest module and install it, if it doesn't).
Create 05_Packages directory on sugon server.
Install the sos package in VM
Run sosreport binary from root. It will create system info file.
Scp the file it had created to the 05_Packages directory on sugon server.
>>>
Create 06_Services catalog on sugon server. All files should reside there.
- Finish all the tasks.
- Save information on the status of the services to text files.
andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ systemctl status srv.mount > srv andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ systemctl status echosrv.service > echosrv
- Upload the files to the 'sugon' server. To copy files to a folder on a remote server, use the 'scp' command:
scp /path/to/local/file username@hostname:/path/to/remote/file scp username1@hostname1:/path/to/file username2@hostname2:/path/to/other/file
For example:andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ scp -P 2131 srv andrey@sugon:/home/andrey/06_Services andrey@sugon's password: srv 100% 472 80.8KB/s 00:00 andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ scp -P 2131 echosrv andrey@sugon:/home/andrey/06_Services andrey@sugon's password: echosrv 100% 447 71.1KB/s 00:00
Note: I do not publish here 'sugon' IP. Please insert the valid IP yourself.
>>>
Get ready for testing!
>>>
…
>>>
Finish all the tasks:
Look at the last task: there's system programming here

Create folder 09_Services2 at sugon.
Put there the updated tcp_echo_serverSR.c file.
- Save systemd journal with events related to the services into text files and upload them to sugon. Hexdump service:
andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ journalctl -u hexdump*service > hexdump.journal
TCP echo service:andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ journalctl -u echosrv.service > echosrv.journal
>>>
Create 10_Network directory on sugon server
- Finish all tasks.
- Write two shell scripts:
base.sh — sets up internal network on base (just 3-4 commands above)
ip link set… — maybe
ip address add …
sysctl …
iptables …
clone.sh — sets up internal network on clone (just 3-4 commands)
ip link set… — maybe
ip address add …
ip route add …
/etc/resolv.conf will be overwritten, so you need to add something like echo nameserver 1.1.1.1 > /etc/resolv.conf to your script
- reboot both VMs
run base.sh on base
run clone.sh on clone
check if host ya.ru is working on clone (that means network is working)
Scp 4 files on sugon server in 10_Network directory:
base.sh
base.log — the output of ip a command on base
clone.sh
clone.log — the output of ip a command on clone
>>>
Log in to sugon and create a folder named 11_ApplicationBus.
- Finish all the tasks on VE
- Listen to D-bus messages with 'dbus-monitor'. In the first terminal, run 'dbus-monitor' to listen to messages:
andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ dbus-monitor | grep -A 10 -B 4 "Hello world"
In the second terminal, send a notification:andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ notify-send "Hello world"
Save what was recorded by 'dbus-monitor' to the 'notification.log' file and upload it to 'sugon'. - Listen to D-bus messages with 'dbus-monitor' to know the call that changes wallpaper.
- Run 'dbus-monitor':
andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ dbus-monitor | grep -A 10 -B 10 "last-image"
- Change the desktop wallpaper.
- Find the method call that changes wallpaper in the 'dbus-monitor' output.
- Based on the call description from 'dbus-monitor' write a command that changes the wallpaper using 'qdbus'. Hint: andrewt@comp-core-i7-3615qm-0dbf32 ~ $ qdbus org.xfce.Xfconf bla-bla-bla
- Save the command to the 'wallpaper.sh' file and upload it to sugon.
- Run 'dbus-monitor':
Modify the server.py service. Add a new method: Signature:
<method name='MultiString'> <arg type='s' name='a' direction='in'/> <arg type='u' name='num' direction='in'/> <arg type='as' name='response' direction='out'/> </method>Body:def MultiString(self, s, num): """returns n strings""" return s * num
Save the program itself and the output (to the 'miltistring.log') and save it to sugon.
>>>
Finish all unfinished programs. Create the 12_HighLevelLanguages folder at the sugon server. Put all programs there.
Home tasks
Task 03
Task 04
Task 05
Task 06
Task 07
Bonus task
Bonus task (if done) should reside in 13_Bonus subdirectory on sugon server. Put there all the files related to your solution, including the prigram itself and 1-million digits pi file it used.
Never use float numbers if you want to achieve precision!
- Preliminaries:
Take look on Chudnovsky Pi calculation algorithm.
$$ \frac{(640320)^{3/2}}{12\pi}=\frac{426880\sqrt{10005}}{\pi} = \sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \frac{(6k)! (545140134k + 13591409)}{(3k)!(k!)^3 (-262537412640768000)^{k}} $$
Learn Python decimal data type.
How to control precision with getcontext().prec = precision (see example at the very start of documentation)
Donwload 1-million precise $$\pi$$ representation (e. g. form here)
- Remove all non-numeric characters from it
- Actually we need no more than 40000 digits for ordinary CPU
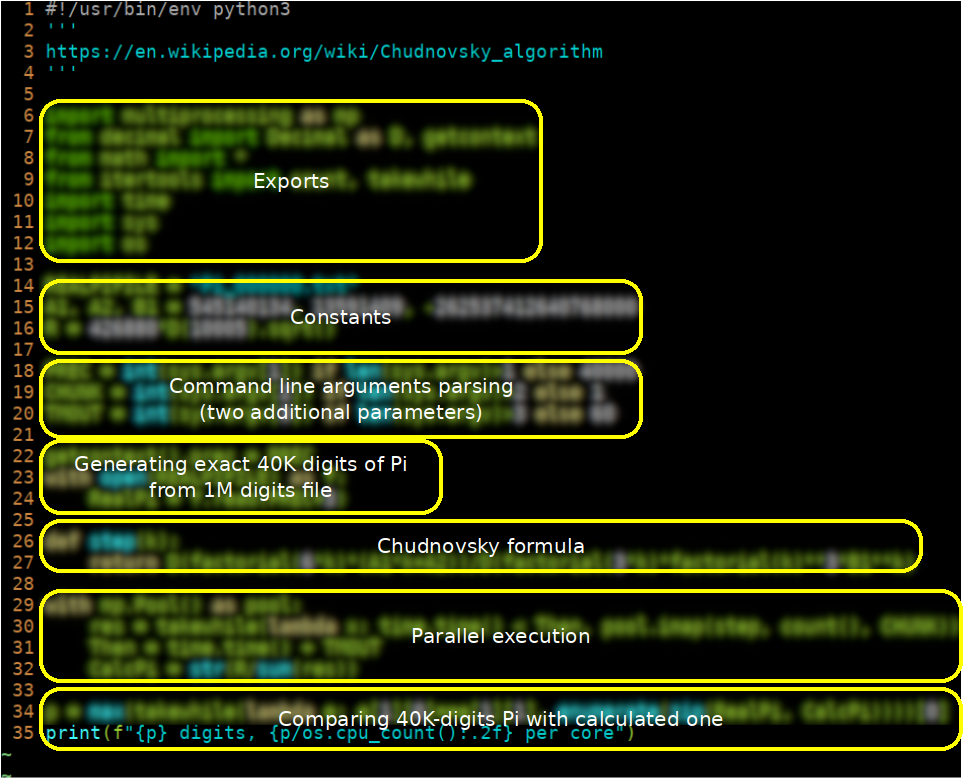
(still no bonus ☺) Write a python program PiChud.py N that iterates over Chudnovsky formula N times and prints out how many exact digits from real $$\pi$$ it has calculated:
george@inspiron:~/src> python3 PiChud.py 4 57 george@inspiron:~/src> python3 PiChud.py 40 568 george@inspiron:~/src> python3 PiChud.py 400 5674
This program calculated 75, 568 and 5674 exact $$\pi$$ digits on 4, 40 and 400 iterations of Chudnovsky formula respectively. Your results and time may differ.
Use 40000 digits Decimal precision
- Make sure you're useng only integers and Decimals and no floats
(bonus) Use miultiprocessing to speed up calculations about N times, when N is the number of cores on your computer. Call the resulting program PiChudP.py
- N can be actually lesser than number of cores. E. g. on 12-core CPU under Linux:
george@inspiron:~/src> time python3 PiChud.py 800 11347 python3 PiChud.py 800 19,94s user 0,01s system 99% cpu 19,952 total george@inspiron:~/src> time python3 PiChudP.py 800 11347 python3 PiChudP.py 800 24,00s user 0,11s system 1002% cpu 2,406 total
Parallel version took more userspace CPU time than single-process (24.00s over 19.94s)
- Parallel version worked 8 times faster than single-process (2.406s over 19.952s)
- N can be actually lesser than number of cores. E. g. on 12-core CPU under Linux:
(more bonuses). Rewrite the program (call it PiChudPA.py) to work N seconds exactly and then stop calculating. Print digits per CPU core statistic (use os.cpu_count()):
george@inspiron:~/src> python3 PiChudPA.py 60 33626 digits, 2802.17 per core
Teaser: this is my solution of bonus task № 2. Note you probably will finish with slightly lager code